why do we conduct soil permeability field tests|permeability of soil sample problems : ODM Soil permeability (hydraulic conductivity) is the rate at which water flows through soil materials. It is an essential characteristic across a broad spectrum of engineering and earth-science . 16 de jan. de 2024 · Braga Wind forecast. Wind direction is South, wind speed varies between 2.2 and 15.6 mph with gusts up to 37.9 mph. The sky is cloudy with a chance of rain 100%. Wind and wave weather forecast for Braga, Portugal, Portugal contains detailed information about local wind speed, direction, and gusts. Wave forecast includes wave .
{plog:ftitle_list}
30/06/2020 09h30 - Atualizado em 30/06/2020 12h51. Estadão Conteúdo Seleção Brasileira de 2002: a única campeã do mundo com 7 vitórias em 7 jogos. O Brasil conquistou o seu pentacampeonato da Copa do Mundo .
Field measurements of soil permeability are used for environmental projects or when designing leach fields for septic systems. The simplest “perc” tests are run by filling a hole with water . The main reason for this is that field tests would work on a large sample where ‘macro permeability’ through layers where natural fissures and soil cracks may occur. Laboratory size samples will not be large enough to .Soil permeability (hydraulic conductivity) is the rate at which water flows through soil materials. It is an essential characteristic across a broad spectrum of engineering and earth-science .Standardized soil permeability tests help assess site drainage capacities and seepage losses for various geotechnical applications. This overview covers common soil permeability test methods, result interpretations, and key .
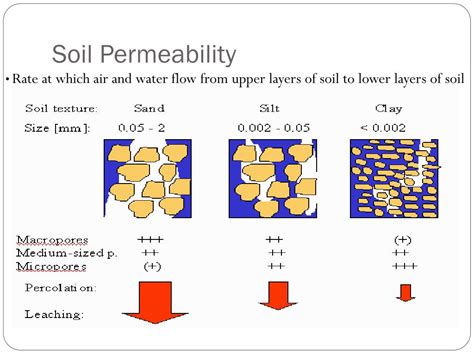
Soil permeability is the quality of a soil enabling it to transmit air or water through the soil pores. Texture, structure, cracking, and the amount of organic matter influence the . Field testing for soil permeability can involve simple percolation tests, where a hole is filled with water and the time it takes for the water level to drop indicates permeability. More reliable field test methods, like pump .
Methods of measuring permeability in the field—borehole tests, pressure dissipation tests, grain size tests, seasonal variation in groundwater levels and pumping tests—are discussed.PERMEABILITY TEST METHOD A. SCOPE. The permeability test is a measure of the rate of the flow of water through soil. In this test, water is forced by a known constant pressure through a soil specimen of known dimensions and the rate of flow is determined. This test is used primarily to. determine the suitability of sands and gravels
Also, a wide range of alternative septic systems have been developed in recent years for use on almost any type of site. Find out which systems are approved for use in your area and which might be suitable for .Overview of Laboratory Methods Testing Soil Permeability. The most accurate permeability measurement technique involves laboratory constant head testing per ASTM D2434 standards using specialty columnar chambers allowing . Permeability Test of Soil. Scope. Apparatus. Procedure. (a) Falling head permeability test. (b) Constant head permeability test. Computations. 1. The falling head permeability test, 2. The constant head permeability test, Results. Discussion. Demerits of Permeability Test. (Laboratory).
The constant head permeability test is a laboratory experiment conducted to determine the permeability of soil. The soils that are suitable for this tests are sand and gravels. Soils with silt content cannot be tested with this method.The test can be employed to test granular soils either reconstituted or disturbed. In this test the differential pressure (the head) across the sample remains constant throughout the test. This permeability test is equally valid for gravel, sands, and clay soils. Field Testing Field testing can also be carried out. These are usually simple percolation tests where a hole is bored and filled with water. Simple Field Percolation Test – measuring the rate of drop in water level in an accurately sized hole enables calculation of saturated soil conductivity, an indicator of soil permeability. Field tests often provide more accurate results than laboratory tests because they account for larger samples and natural variations in soil, such as .
Field CBR Test. Field CBR testing is performed in-place on soil subgrades to determine in-place conditions of soils and bases or to confirm laboratory test results. The ASTM D4429 test method requires special CBR field equipment for loading. Soil saturation can be controlled in the laboratory but not in the field, so it is difficult to make a . Different types of soil testing. The types of soil test depend on the soil texture and quality. Methods used for testing soil include Lab Test and Field Test: Lab Test: 1. Moisture Content Test: Moisture content test gives all information about moisture or water content of the soil. The information about water table will provides detailed .
Particle size is one of the criteria used to ascertain whether the soil is suitable for building roads, embankments, dams, etc. Information obtained from particle size analysis can be used to predict the soil-water movement if the permeability test is not available. Objective. To obtain the grain size distribution curve for a given soil sample.
In addition, the soil is compacted in 5 layers with 25 blows per layer. The test is conducted for 5 moisture contents to obtain the optimum water content (w opt), for which the value of the dry unit weight is maximum (γ d,max). Test Equipment. The equipment utilized to .9.5 Measurement of soil permeability in the field . To measure soil permeability in the field, you can use one of the following tests: The visual evaluation of the permeability rate of soil horizons; A simple field test for estimating soil permeability; A more precise field test measuring permeability rates. Permeability Testing - There are several laboratories and in situ tests that can be done to estimate the permeability of the soil and every test has its own advantages and disadvantages. . This method is recommended when we have a coarse granular soil such as sand, where the quantity of discharge of liquid through the sample is large. .
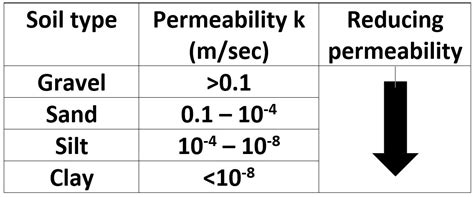
typical permeability values of soil
9.5 Measurement of soil permeability in the field . To measure soil permeability in the field, you can use one of the following tests: The visual evaluation of the permeability rate of soil horizons; A simple field test for estimating soil permeability; A more precise field test measuring permeability rates.
FIELD MANUAL 110 Table 17-1.—A glossary of abbreviations and definitions used in permeability calculations K = Coefficient of permeability in feet (meters) per year under a unit gradient. Q = Steady flow into the well in ft3/sec [m3/sec]. H = The effective head of water in the well in feet (m). For packer tests, determining the effective head is definedWhen clay minerals are present in fine-grained soil, the soil can be remolded in the presence of some moisture without crumbling. This cohesiveness is caused by the adsorbed water surrounding the clay particles. At a very low moisture .1 Determination of Moisture Content Introduction. The moisture content of soil also referred to as water content, is an indicator of the amount of water present in soil. Moisture content is the ratio of the mass of water contained in the pore .
Methods of measuring permeability in the field—borehole tests, pressure dissipation tests, grain size tests, seasonal variation in groundwater levels and pumping tests—are discussed. The methods are compared by reference to work done on actual sites, in particular on a site which involved the design and construction problems for a dam on a .
When a load is applied in a low permeability soil, it is initially carried by the water that exists in the porous of a saturated soil resulting in a rapid increase of pore water pressure. This excess pore water pressure is dissipated as water drains away from the soil’s voids and the pressure is transferred to the soil skeleton which is . A perc test, or percolation test, is a procedure performed by a trained professional to test the absorption rate of the soil. Learn when you might need one. Search for:A horticulture student taking a soil sample in a garden near Lawrenceville, Georgia. A soil test is a laboratory or in-situ analysis to determine the chemical, physical or biological characteristics of a soil. Possibly the most widely conducted soil tests are those performed to estimate the plant-available concentrations of nutrients in order to provide fertilizer recommendations in agriculture.Tests in boreholes only involve a relatively small volume of soil or rock around the test section - these tests provide ‘small-scale’ values of permeability. If the soil/rock is heterogeneous or has significant fabric, such tests may not be representative of the mass permeability of the strata.
What are the reasons why we conduct field tests of soil permeability versus relying solely on the results of laboratory testing. Define permeability in soil. QUESTION 5 Structures located _________ the groundwater table are subjected to _________pressure from . Field permeability tests offer another technique for measuring permeability without sample disturbance making it more suitable for granular soils. However, it is difficult to evaluate the hydraulic gradient acting on the soil during field permeability tests. Furthermore, most methods of permeability calculation from field tests are .
The permeability test is carried out on a cylindrical test specimen that is either confined laterally by a rigid container or by a flexible membrane. The specimen is subjected to differential hydraulic head and the water flow is measured under either a constant or falling head.
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ What are the reasons why we conduct field tests of soil permeability versus relying solely on the results of . What are the reasons why we conduct field tests of soil permeability versus relying solely on the results of laboratory testing. Define permeability in soil. loading. See answer.Permeability test is also unavoidable soil tests for construction. It is conducted to determine the coefficient of permeability of the sample of the soil taken. Permeability of soil can be tested from two methods: Falling head method (used for fine-grained soil) Constant head method (used for coarse-grained soil) Falling head method. Apparatus .
typical permeability of soils

Samuel Joslin is an actor born in 2002 in London, England, UK. He is known for his roles in The Impossible (2012), Paddington (2014) and Paddington 2 (2017). Learn more about .
why do we conduct soil permeability field tests|permeability of soil sample problems